There are two types of structures that businesses can be organised in: tall & flat.

A hierarchy shows the layers of management and authority in a business or enterprise.
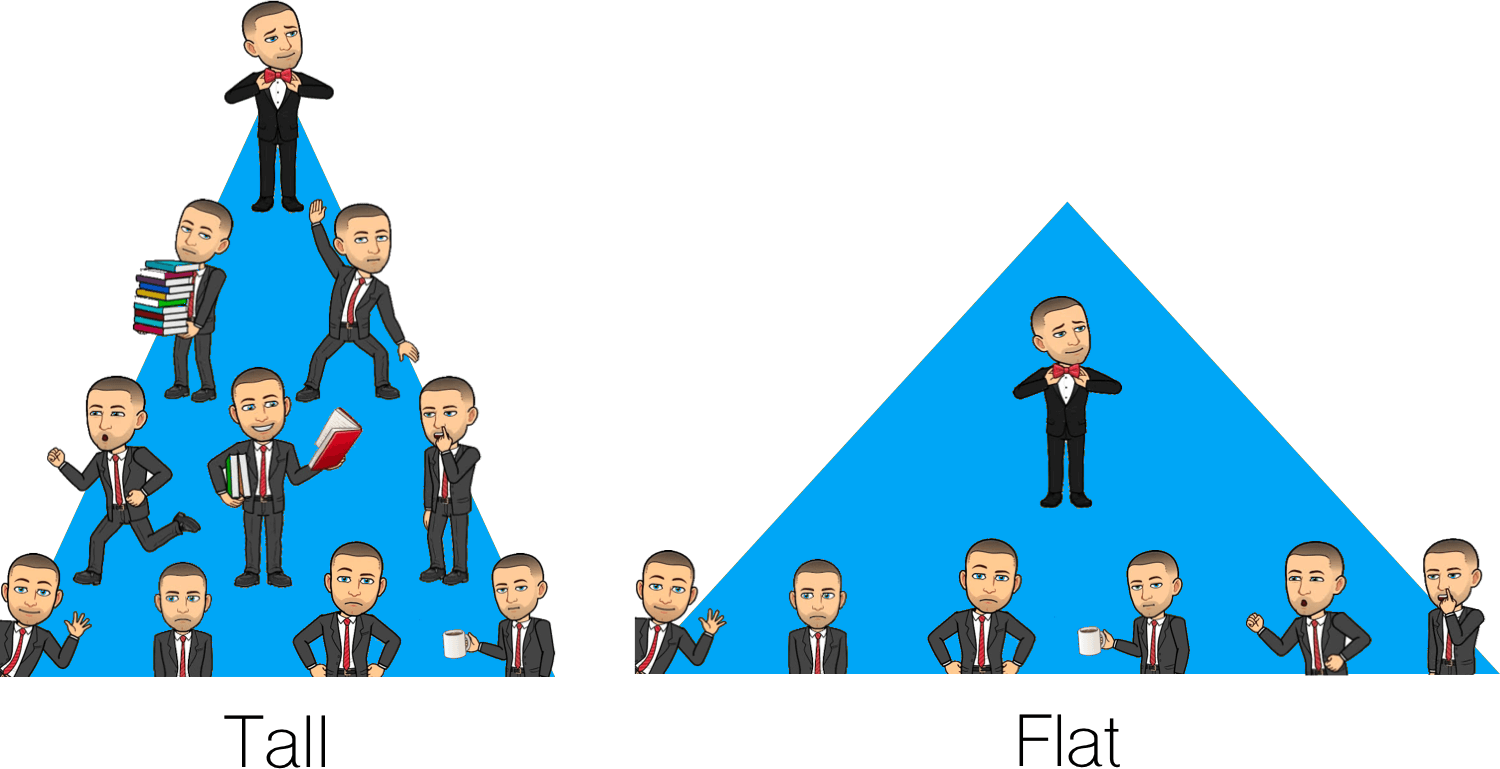
Tall organisations have many layers of management in its organisational hierarchy.
Flat Organisations have few layers of management in its organizational hierarchy.
Delegation is the assignment and entrustment of tasks to another person below you in the hierarchy.
Chain of command is the route/line of communication and authority within a business, it shows the route an order takes to get to its intended recipient.
Layers are the different levels of employees or management in the organisation.
Span of Control is the number of people a manager is directly responsible for (only directly under).
Subordinates are the people below a manager in the hierarchy. E.g. salesperson is a subordinate of the head of sales.
Remember for the exam:
Tall Organisation

- Many layers in hierarchy
- Narrow span of control — managers are responsible for few people, less opportunity for delegation
- Long chain of command – decision-making and communication can take a long time to make decisions as information have to be passed up and down the hierarchy
- Many opportunities for promotion — workers can move up the organisation to get more authority
Advantages
+ Opportunities for promotion for staff
+ Higher standards and consistency as decisions are made at the top
+ High levels of control — easier to check work at each level
Disadvantages
– Poor communication between top and bottom as there may be too many layers
– Slow decision-making
– less delegation of tasks to subordinates
– Split between management and workers
Flat Organisation

- Few layers in hierarchy
- Wide span of control – managers are responsible for many people, more delegate of tasks to subordinates
- Short chain of command – decision-making and communication is fast and workers at the bottom have more authority and more power to make decisions and there are fewer people to pass information up to
- Few opportunities for promotion — less room for employees to move up the hierarchy
Advantages
+ Fewer managers so lower costs
+ Staff have more responsibility so may be more satisfied
+ More opportunities for delegation of tasks from manager to subordinate
+ Quick communication up and down the organisation
Disadvantages
– Managers are responsible for many staff members so have to delegate more work
– Low level of control as workers lower down have more authority
– Workers may lack experience but have more decision-making power so consistency may be lacking or mistakes made
Delegation
Delegation happens when a manager entrusts tasks to someone below them (subordinates) in the hierarchy to complete. Delegation happens more in flatter organisations as managers have more subordinates to assign responsibilities to.
Advantages
+ managers can reduce workload and stress
+ subordinates may feel motivated as they have more responsibility
+ efficient use of staff downtime when subordinates are not busy
+ allows employees to train on the job for more senior roles
+ managers can focus on important jobs
Disadvantages
– subordinates may feel pressured or stressed with extra tasks
– subordinates may be inexperienced or unqualified to complete the job
– hard to delegate in small or tall businesses as key information is lost in a long chain of command
– some jobs and tasks are not suitable for delegation
Task
Complete the test here.




